Archives
-
April (In Progress)
Vol. 20 No. 1 (2026) -
March (In Progress)
Vol. 19 No. 3 (2026) -
February
Vol. 19 No. 2 (2026) -

January
Vol. 19 No. 1 (2026)Cover image by Zhaohui Lu on pages 1–13. The image illustrates how injected CO2 migrates through the fracture–matrix system in normal-pressure marine shale gas reservoirs, displacing adsorbed CH4 via competitive adsorption while achieving geological storage. Through integration of experiments, numerical simulation, and China’s first pilot test, the study identifies optimal operational parameters for CO2 huff and puff, offering a robust basis for enhancing recovery in depleted normal-pressure shale gas wells.
-
December
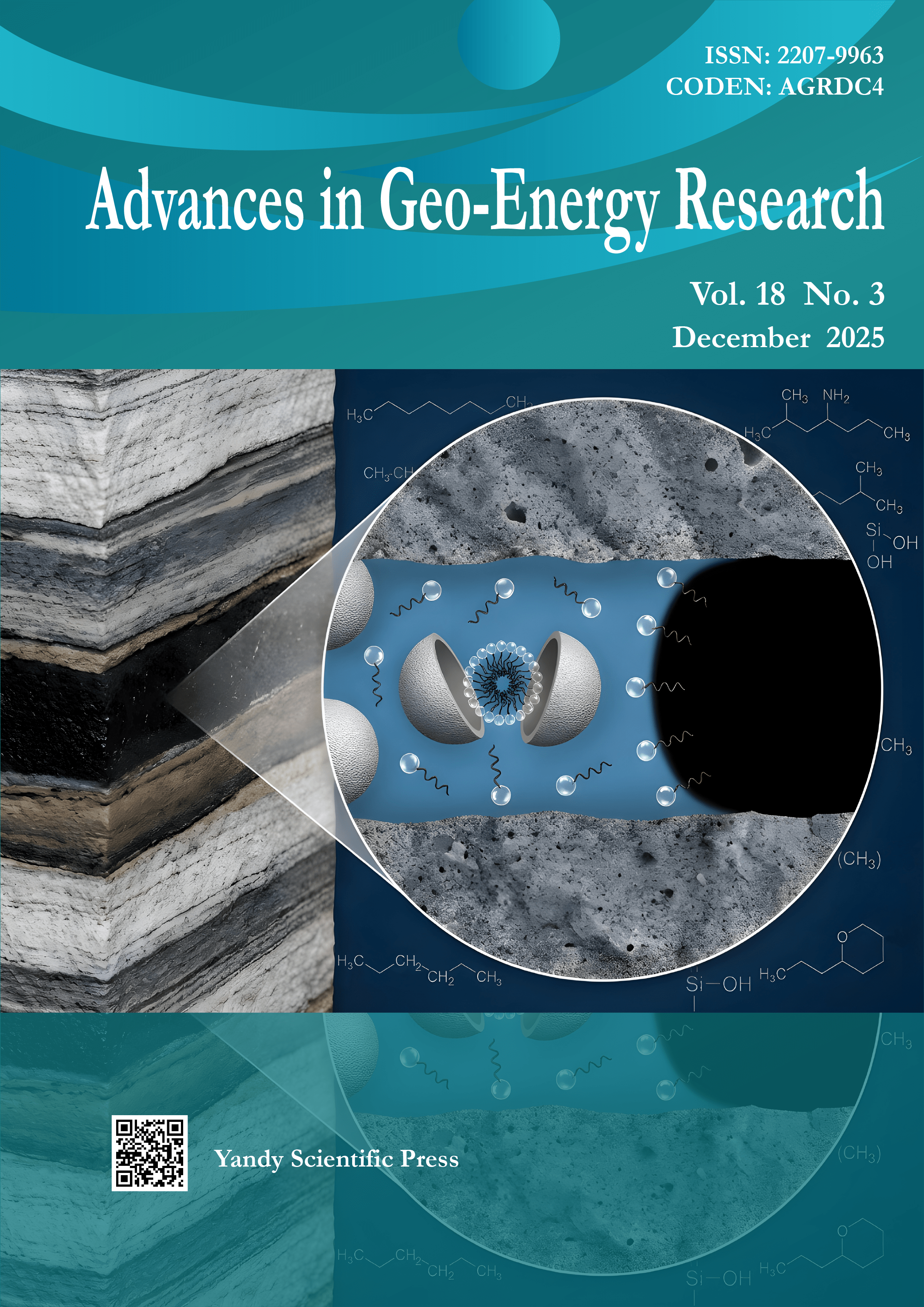
Vol. 18 No. 3 (2025)Cover image by Chengdong Yuan on pages 272–286. The image illustrates encapsulated surfactants for enhanced oil recovery, featuring silica nanocarrier-assisted surfactant delivery in porous media. Controlled surfactant release from silica carriers reduces adsorption while enabling synergistic effects at the oil–water–rock interface through the co-presence of released surfactants and silica nanoparticles. This enhances interfacial and wetting performance and improves displacement efficiency during chemical enhanced oil recovery.
-

November
Vol. 18 No. 2 (2025)Cover image by Junping Zhou on pages 180-194. The image illustrates that CO2 injection into a shale gas reservoir not only disrupts the thermo-hydro-mechanical equilibrium but also induces geochemical reactions leading to mineral dissolution and weakened mechanical properties, which in turn affect the interactions among various physical fields. Consequently, accounting for the thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical coupling effects is crucial for assessing the efficiency of CO2-enhanced shale gas recovery.
-

October
Vol. 18 No. 1 (2025)Cover image by Liu Yang on pages 21-37. This figure illustrates the investigation of spatiotemporal mechanical evolution of conglomerate during CO2 sequestration using micro-scratch technology. CO2-water-rock interaction forms a pore-fracture network due to mineral dissolution and weakening reservoir strength. This is of great significance for evaluating the mineralization sequestration mechanism of glutenite reservoirs and assessing sequestration safety.
-

September
Vol. 17 No. 3 (2025)Cover image by Quanyou Liu on pages 256-266. The image illustrates the process by which a fault, after its formation, develops sealing capabilities that prevent fluid migration between its two sides. Through mechanisms such as rotation, rolling, cracking, and cataclasis of the host rock particles, the fault forms with both porosity and permeability lower than that of the host rock, thereby acting as a barrier to fluid flow. These effects elucidate the relationship between fluid migration and fault sealing capacity during the formation and evolution of faults.
-
August
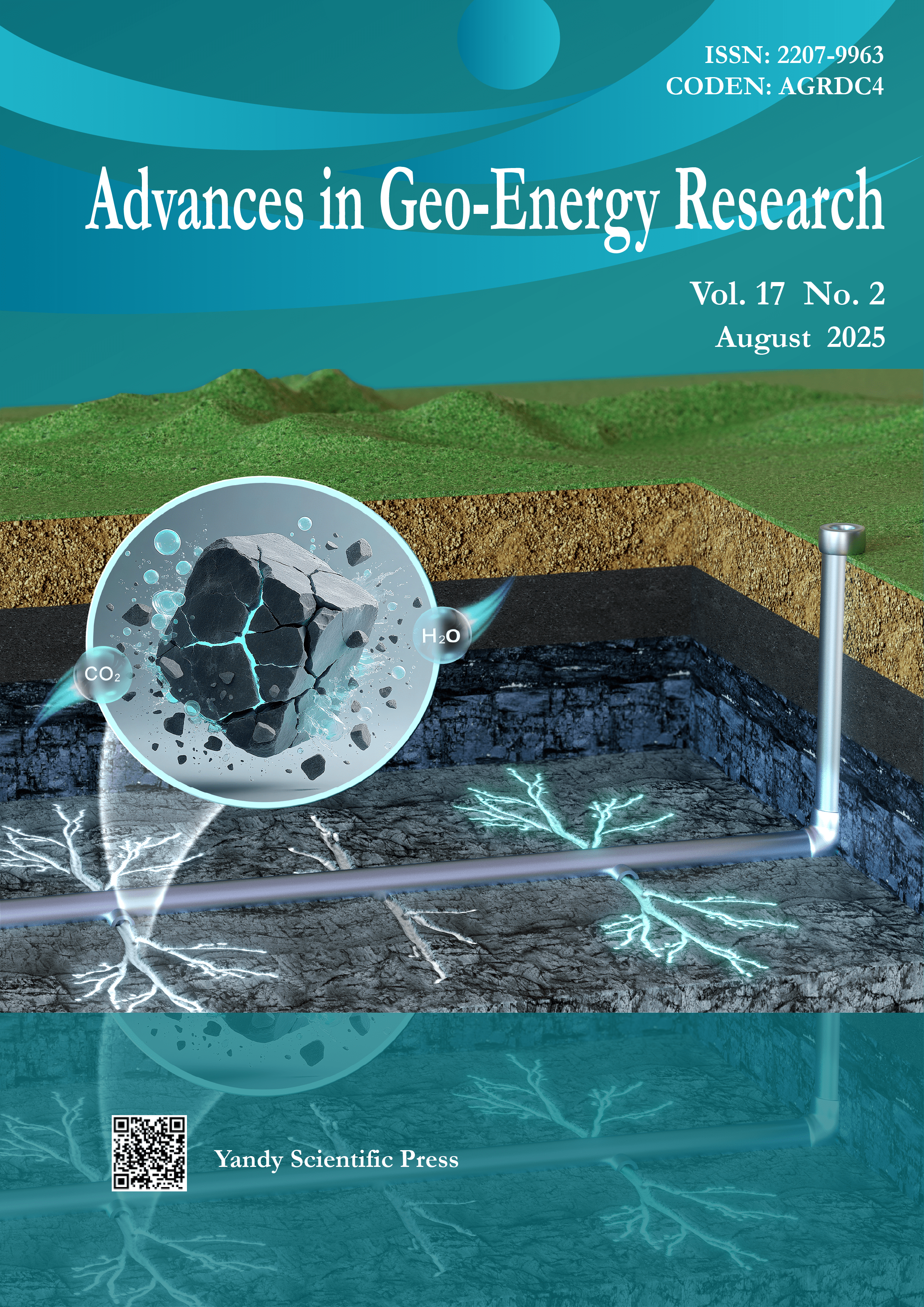
Vol. 17 No. 2 (2025)Cover image by Bo Wang on pages 95-106. The image illustrates physical and chemical coupling during CO2 fracturing in dense reservoirs. The aqueous solution of CO2 dissolves minerals in the rock, forming dissolution pores and micro-fractures. CO2 fracturing creates a complex and deep fracture network. These effects explain enhanced production by CO2 pre-fracturing during dense reservoir stimulation.
-

July
Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025)Cover image by Caineng Zou on pages 68-81. This image illustrates the secondary reconstruction of marine shale through water-rock interaction. Hydration and dissolution of minerals not only generate abundant secondary pores and fractures but also weaken rock mechanical strength, thereby facilitating the evolution of pore-fracture networks. The key role of water-rock interaction in reshaping reservoir characteristics is emphasized.
-
June
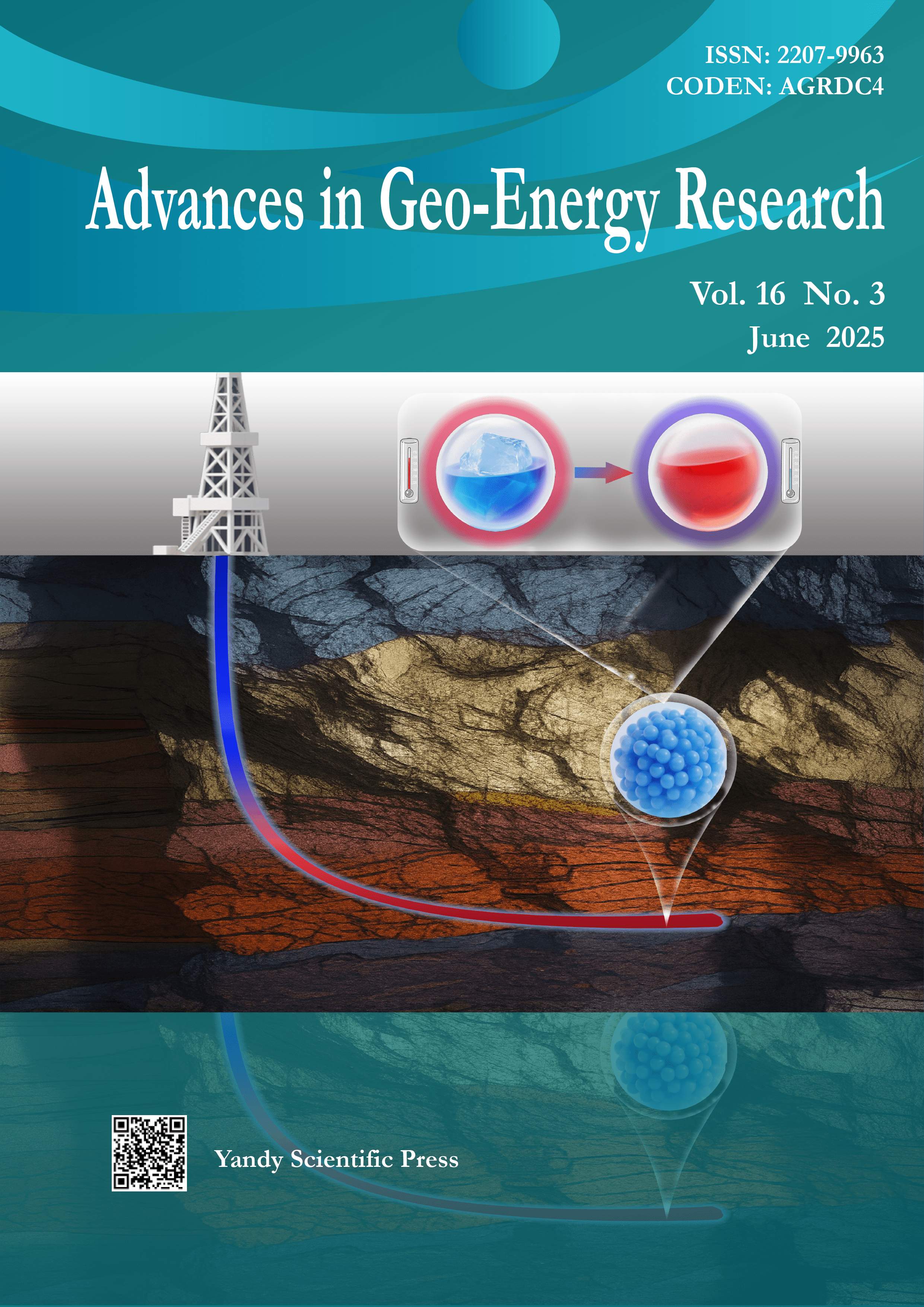
Vol. 16 No. 3 (2025)Cover image by Mei-Chun Li on pages 211-228. The image illustrates the cooling effect of phase-change microcapsules in a high-temperature wellbore. When the temperature exceeds the phase-change threshold, the core material melts, absorbing significant heat and thereby reducing the drilling fluid temperature. This thermal regulation improves drilling efficiency and operational safety.
-
May
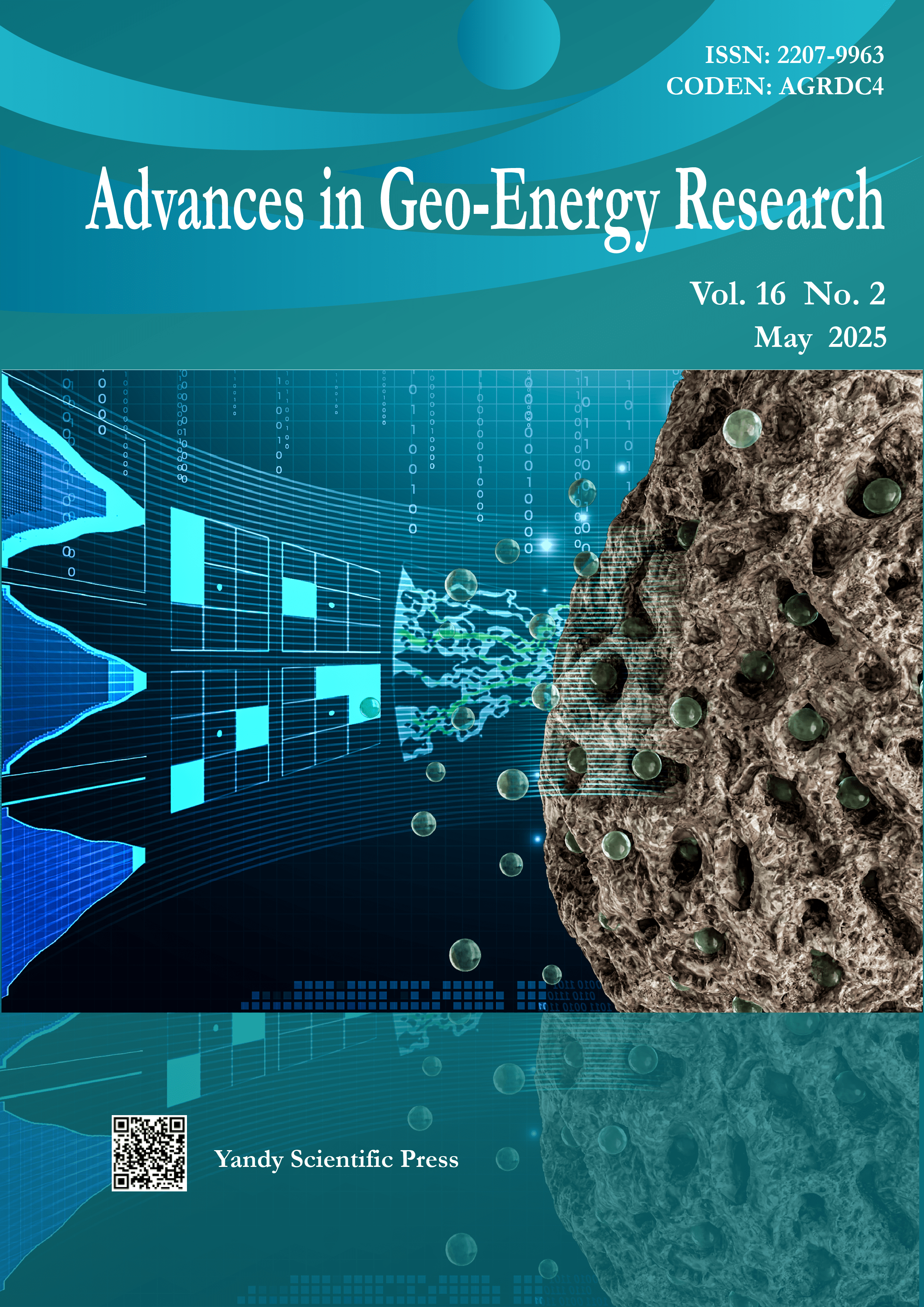
Vol. 16 No. 2 (2025)Cover image by Saman A. Aryana on pages 143-157. This image illustrates a computational framework for simulating gas transport in confined porous media. On the right, a porous structure highlights the complexity of meso- and micro-scale pore networks. The central portion transitions into a digital representation of gas transport pathways, modeled using a multi-block lattice Boltzmann approach. The left side features computational grids, slip boundary conditions, and a scale-informed grid refinement strategy.
-
April
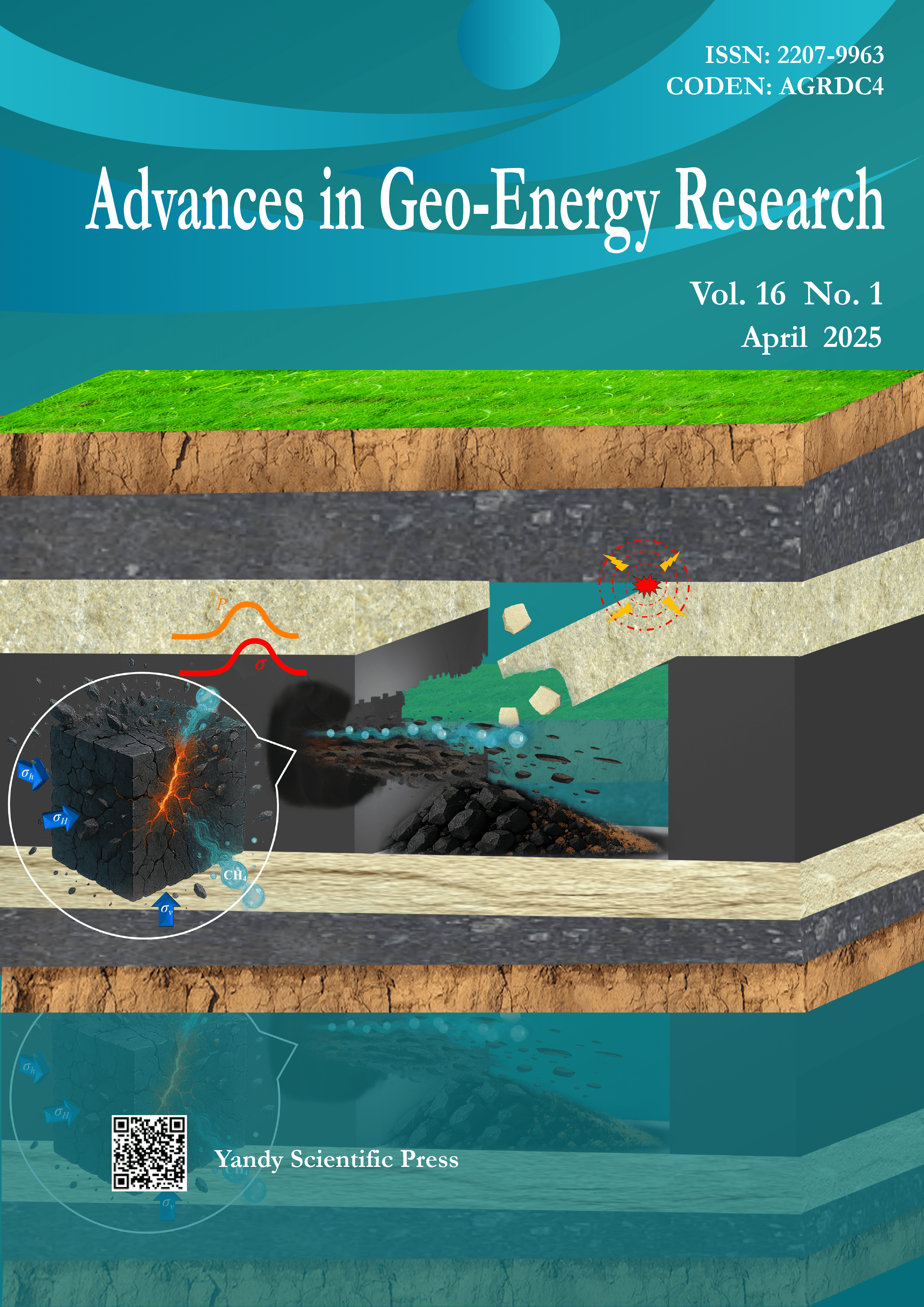
Vol. 16 No. 1 (2025)Cover image by Jupeng Tang on pages 60-76. The image illustrates the dynamic evolution process of compound dynamic disasters during deep coal mining. Disasters are induced by gas and stress loading and unloading, and the effects of AE energy, temperature and impact force in the process of disaster incubation are evaluated to differentiate behaviors among disaster types. The deep coal rock outburst-rockburst mutual induction and transformation mechanism is revealed.
-
March
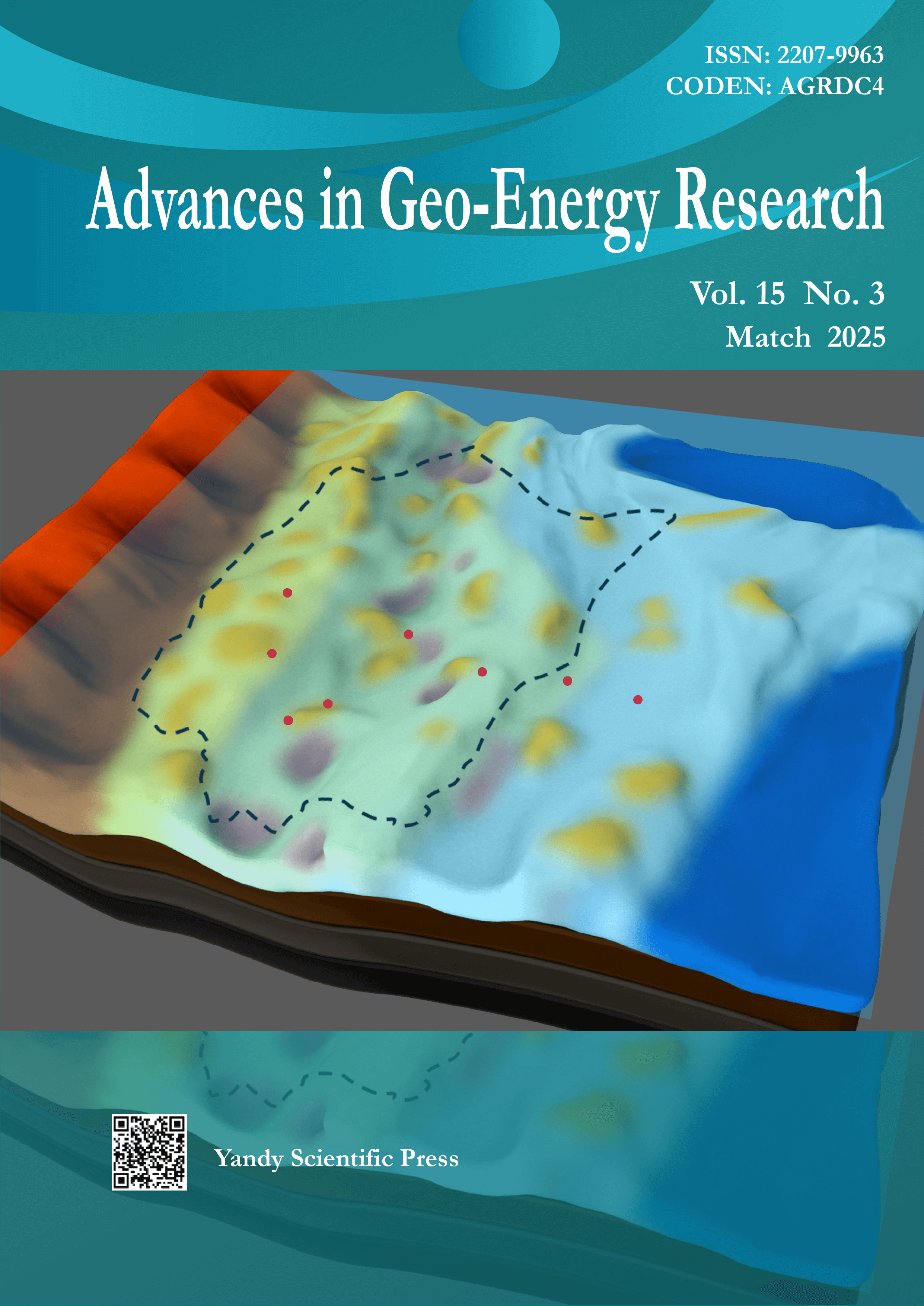
Vol. 15 No. 3 (2025)Cover image by Jinmin Song on pages 216-229. This image illustrates the three-terraced evaporated ramp model for differentiation of the massive dolomitization process in the lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in the Sichuan Basin. Through meticulous field observations, petrological examinations and geochemical analyses, the correlation between the distribution of dolostones and paleogeomorphological features has been elucidated, and a three-terraced evaporated seepage reflux dolomitization model has been proposed.
-

February
Vol. 15 No. 2 (2025)Cover image by Yan Jin on pages 158-171. The image illustrates the process of wellbore instability analysis and control while drilling. A new method for wellbore instability analysis and control is proposed by combining image recognition methods with expert systems. The method applies an image recognition model improved by multi-source feature fusion to identify caving types and establishes an expert system model that correlates caving types with wellbore instability mechanisms.
-
January
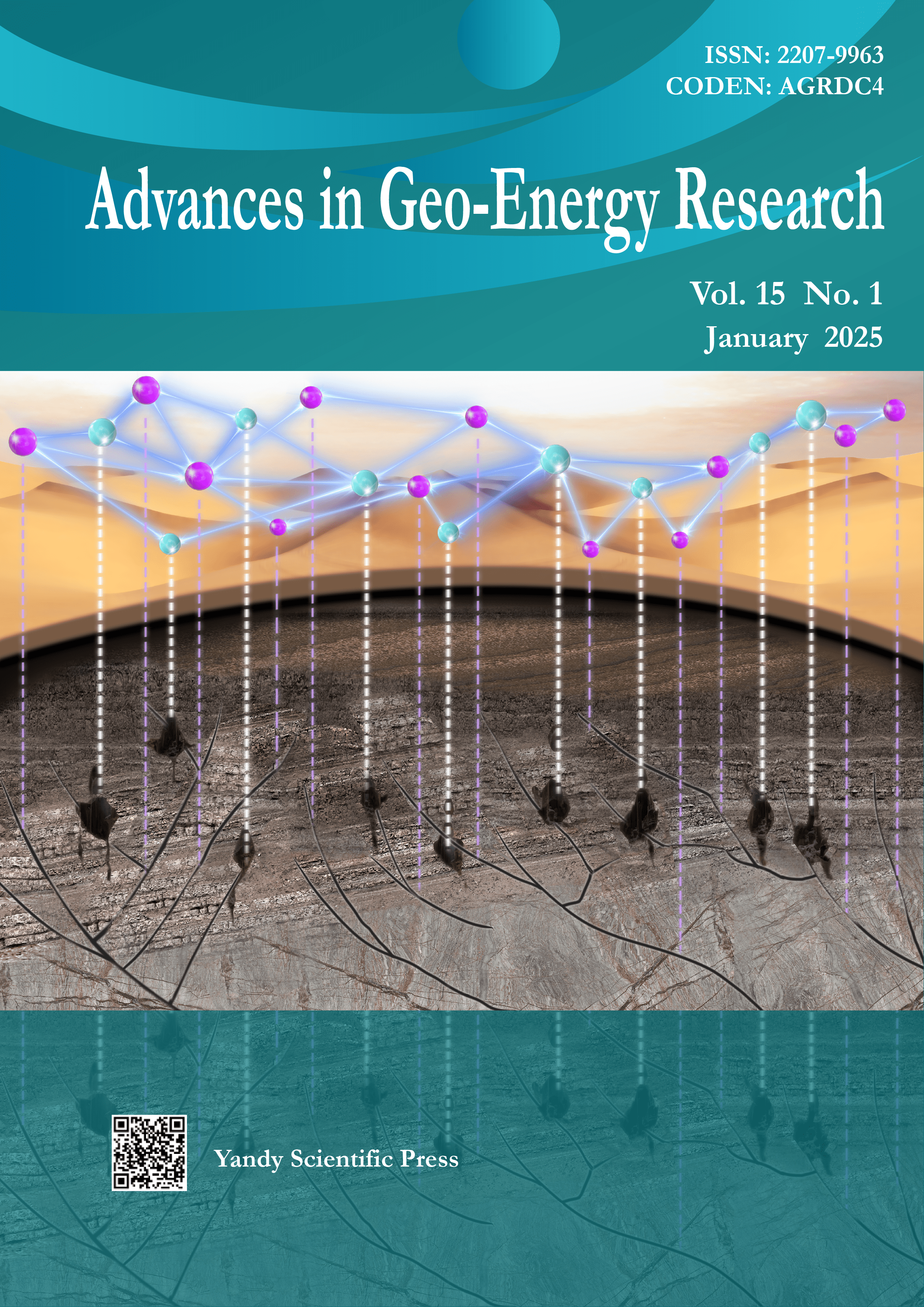
Vol. 15 No. 1 (2025)Cover image by Hanpeng Cai on pages 68-78. The image illustrates the process of utilizing a knowledge graph to represent underground faults and karst caves, as well as the relationships between them. By modeling faults and karst caves as entities and their relationships as edges, a fault-karst cave graph is constructed. This facilitates systematic analysis, producing reservoir unit divisions that align with seismic data and providing a novel approach for multi-element integrated analysis in geophysical exploration.
-

December
Vol. 14 No. 3 (2024)Cover image by Gang Wang on pages 187-200. The image illustrates the process of cutting and scanning water injected coal using Cryo-FIB-SEM technology. Cryo-FIB-SEM technology provides a new idea for this challenge, which is to freeze the water into small and uniform ice crystals without damaging the coal structure, and then perform high-precision scanning, combined with image processing technology to achieve three-dimensional observation of water in coal.
-

November
Vol. 14 No. 2 (2024)Cover image by Yunyi Qian on pages 106-118. The image illustrates seismic events on slip faults induced by stress unloading during geo-energy extraction. As extraction of offshore oil and gas platforms reduces reservoir pressure, the surrounding faults may be activated. In these fluid-rich environments, the complex behavior of nearby fault slips is further influenced by extraction activities, highlighting the intricate relationship between geo-energy development and subsurface fault dynamics.
-

October
Vol. 14 No. 1 (2024)Cover image by Heping Xie on pages 12-24. The image illustrates the operation of the deep in-situ condition-preserved coring and testing technique. The enlarged view emphasizes that a solid film is forming during the coring process to preserve the core sample under in-situ conditions. This technique aims to obtain core samples with preserved in-situ conditions and test them in the in-situ environment to obtain their true physical and mechanical properties.
-

September
Vol. 13 No. 3 (2024)Cover image by Yuliang Su on pages 203-217. The image illustrates the microscopic process of CO2 entering the shale heterogeneous porous media in the high temperature and high pressure chamber. When CO2 is injected along the fracture, the formation pressure gradually increases to the condition of oil and gas miscibility, and CO2 molecules will diffuse into the matrix, highlighting the migration of CO2 in the pore structure and the dynamic mechanism of the oil and gas interface during huff-n-huff.